Article 01
Goal
The goal of this research is to develop an FHIR-based microservice platform that integrates HISs and CDSSs into a unified information space.
- HISs: hospital information systems
- CDSSs: clinical decision support systems
Method
Platform Architechture
The CDSS platform was developed as a set of separate services, that is, nodes distributed in groups. Microservices communicate with each other asynchronously using the REST communication protocol.
Services
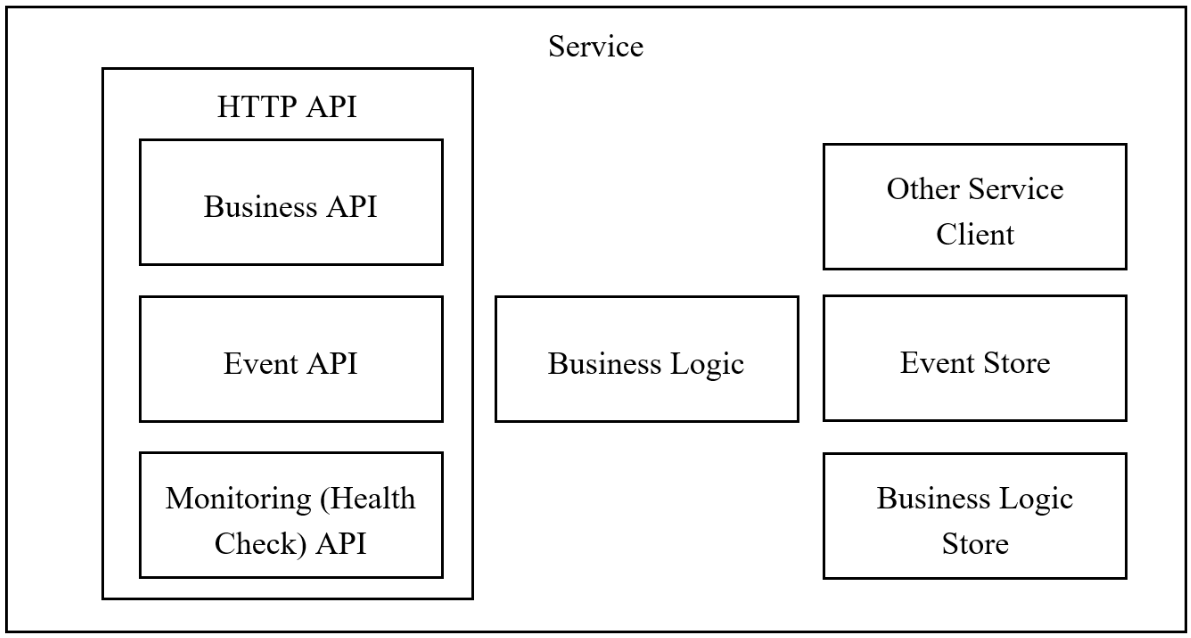 All the services operate through public contracts represented in FHIR JSON format, providing the unique resource identifier (URI) of the resources.
All the services operate through public contracts represented in FHIR JSON format, providing the unique resource identifier (URI) of the resources.
- Business API endpoints allow sending service-specific requests, for example, to return specific artifacts or terminology from the knowledge base.
- Event API endpoint (e.g., HTTP/event) allows an external service to send event requests. So the service knows the status of other services of the platform.
- The Health Check API endpoint (e.g., HTTP/health) returns the health status of the service to its handler to provide continual monitoring. The API endpoint handler performs various checks, such as
- the status of the connections to the infrastructure services used by the service instance;
- the status of the host, for example, disk space;
- application-specific logic.
- Business Logic is the main part of the service that is responsible for the implementation of the feature the service is designed for, for example, the logic of loading facts from the database into an inference engine.
- Event Store and Business Logic Store are responsible for managing and saving data related to the corresponding process of the service.
- Other Service Client is responsible for active communication with other services of the platform, for example, sending the events and the results of the work.
Each service has an independent release cycle, so the public interfaces support versioning to provide consistent operation of the system.
Clinical Modelling
Using Forge to design a set of FHIR profile extensions. Using LOINC (Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes) and SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine—Clinical Terms) to codes to define the semantics of the medical concepts (the codes for the extended fields of FHIR resource profiles).
- A “Patient” was used as the main resource of the platform.
- The platform supports the following FHIR R4 resources as input and output data: CarePlan, MedicationRequest, ActivityDefinition, DetectedIssue, RiskAssessment, Questionnaire, QuestionnaireResponse, ResearchDefinition, PlanDefinition, Goal, Observation, Condition, FamilyMemberHistory, DiagnosticReport, Group, RequestGroup, AllergyIntolerance, Immunization, Procedure, Encounter, Appointment.
Rule Engine
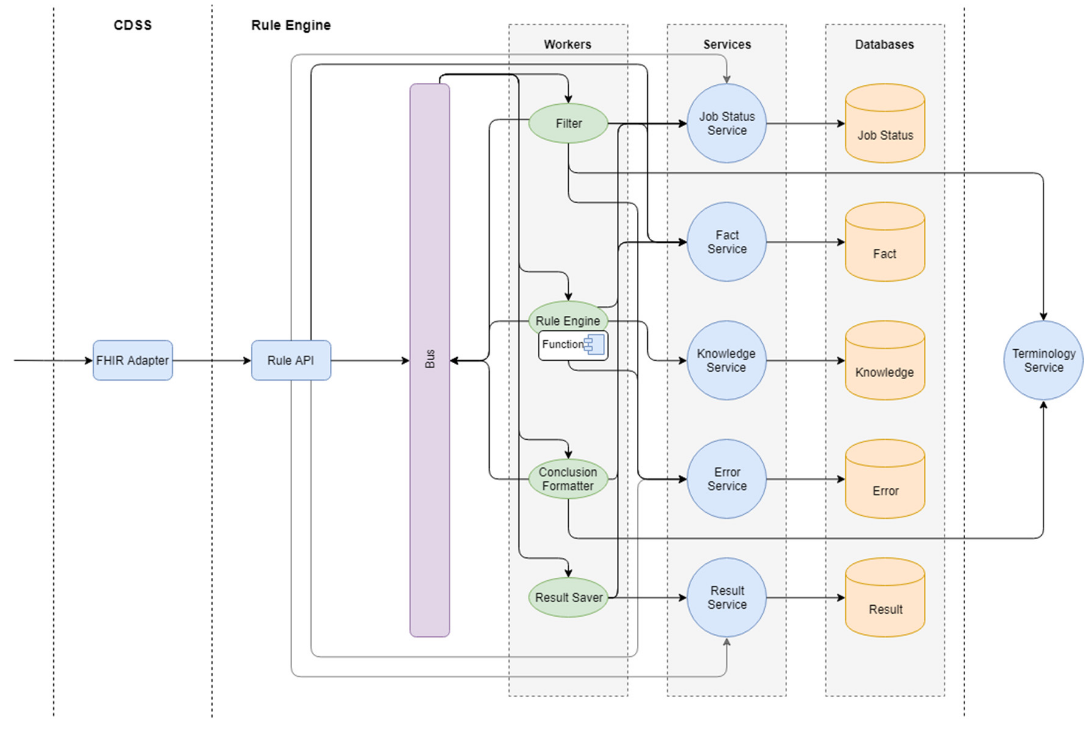
- FHIR Adapter: the service converts data from the FHIR format into the internal Rule Engine format. This service also provides the possibility of Rule Engine invocation according to the CDS Hooks specification.
- Rule API: the service performs internal routing and saves processed data for further analysis.
- Filter: the service is responsible for filtering the data to the actual state, applicable to the mechanism of logical output.
- Rule Engine: the service is responsible for the logical inference mechanism based on the rules.
- Formatter: the service is responsible for formatting the results of logical inference.
- Api.KnowledgeService: the knowledge service is responsible for CRUD operations with the graphical knowledge base. Is used by the Rule Engine to search for rules, artifacts, and definitions.
- Api.FactService: fact service is responsible for preserving and providing facts at all stages of inference.
- Api.JobStatusService: the status service is responsible for creating new tasks and saving statuses.
- Api.ErrorService: the error service is responsible for saving and reporting errors that occur during the inference process.
- Api.ResultService: the result service is responsible for saving and providing the results obtained by the Rule Engine inference.
- TerminologyService is responsible for the storage and provision of medical terminology.
Bayes Engine
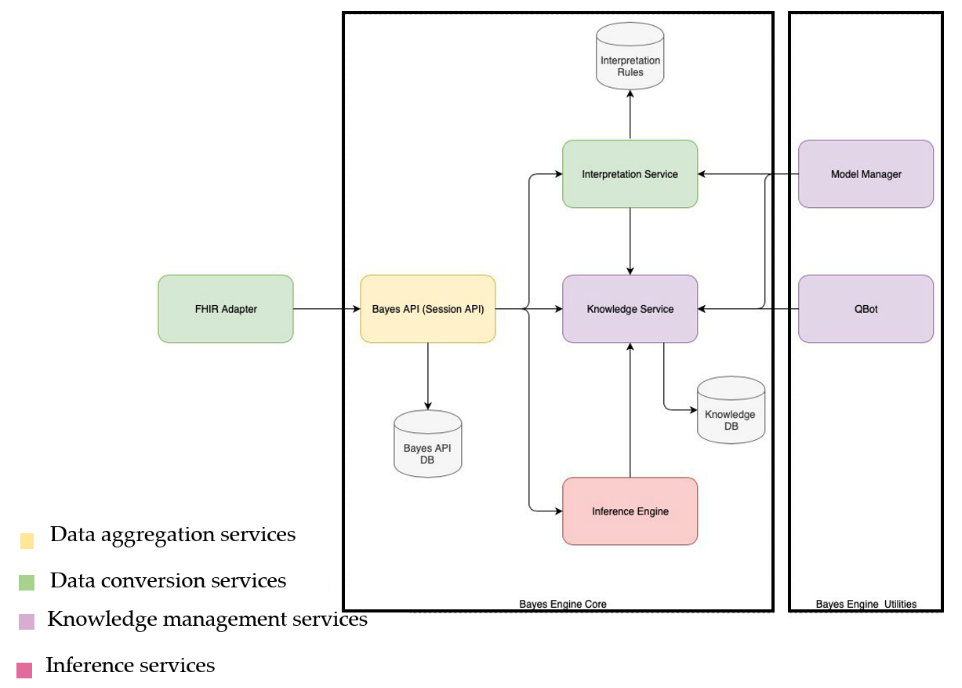
- FHIR Adapter: the service converts data from the FHIR format into the internal Bayes Engine format. Furthermore, this service provides the possibility of Rule Engine invocation according to the CDS Hooks specification.
- Bayes API: the service performs internal routing and stores processed data for further analysis;
- Interpretation Service: the service performs data processing before calculation on Bayesian networks;
- Knowledge Service: the service stores Bayesian models created by experts and collects probabilities used for calculations;
- Inference Engine: the service performs inference on the basis of Bayesian models;
- Qbot: the service validates inference results and models with experts in the learning mode;
- Model Manager: supports model management in the Knowledge Service (CRUD on models).
Impressions
In this article, they more use FHIR standard to transifer EHR data in a standard format (JSON) to microservies platform.
- FHIR Specification
- Build own FHIR resources extensions based on FHIR R4 with URI (Unique resource identifier).
- Extend resources' fields based on LOINC and SNOMED CT.
- Almost 21 FHIR resoruces are used support input and output data.
- FHIR Adapater
- A tool for convert FHIR data to platform services data.
- TerminologyService: the storage and provision of medical terminology.